In an exciting turn of events, an ancient Roman sarcophagus has been unearthed at a construction site in London. This significant archaeological find sheds light on the city’s Roman past and promises to provide valuable insights into the lives and customs of its ancient inhabitants.

The Discovery
The sarcophagus was uncovered during routine excavation work for a new construction project in central London. Archaeologists working on-site were surprised to find the well-preserved stone coffin, which dates back to the Roman period. The sarcophagus was discovered in an area previously thought to be of limited archaeological interest, highlighting the potential for significant finds in urban construction sites.
Features of the Sarcophagus
Design and Craftsmanship: The sarcophagus is made of high-quality stone and features intricate carvings and inscriptions. The detailed artwork includes motifs typical of Roman funerary art, such as floral designs, mythological scenes, and inscriptions that might provide information about the deceased.
Inscription Analysis: Initial examinations of the inscriptions suggest that the sarcophagus belonged to a prominent Roman citizen, possibly someone of high social or political status. The inscriptions could reveal the individual’s name, titles, and possibly their family background.
Construction and Symbolism: The sarcophagus’s design reflects the funerary practices of the Roman period, including the use of elaborate stonework and symbolic decorations. These elements offer insights into Roman burial customs and beliefs about the afterlife.
Implications and Reactions
Historical Insights: The discovery provides a rare and valuable glimpse into London’s Roman past. It can help historians and archaeologists understand the city’s development during the Roman occupation, including aspects of social hierarchy, funerary practices, and urban life.
Archaeological Impact: The find underscores the importance of archaeological assessments in construction projects. It highlights the potential for significant discoveries in urban areas, even in locations that might not initially seem promising for archaeological work.
Public Interest: The sarcophagus has captured the public’s imagination, generating interest in London’s ancient history. The find is likely to be featured in museums and exhibitions, allowing the public to learn more about Roman London and its inhabitants.
Ongoing Research
Detailed Analysis: Experts are conducting a thorough analysis of the sarcophagus, including the stone material, carvings, and inscriptions. This research aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the sarcophagus’s historical context and significance.
Preservation and Conservation: The sarcophagus is being carefully preserved and conserved to prevent any damage during further study and eventual display. Conservationists are working to ensure that the artifact remains in good condition for future generations.
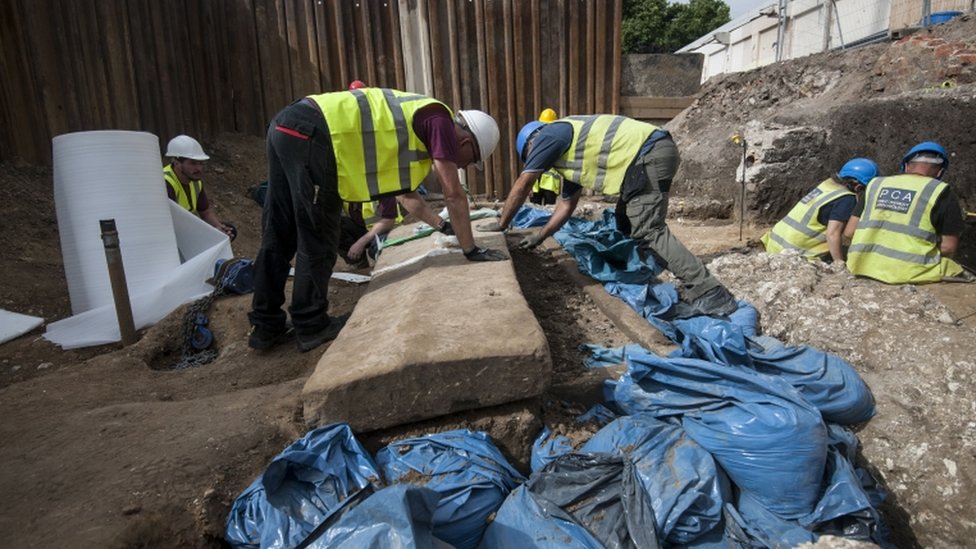

Contextual Exploration: Archaeologists are examining the surrounding area for additional artifacts or structures that might provide more context for the sarcophagus. This includes investigating any related burial practices or associated features from the Roman period.
Conclusion
The discovery of the ancient Roman sarcophagus at a London construction site is a remarkable find that enriches our understanding of the city’s Roman heritage. As research and conservation efforts continue, the sarcophagus is set to offer valuable insights into Roman funerary customs and the lives of its prominent citizens. This find not only enhances our knowledge of London’s ancient past but also highlights the ongoing significance of archaeological exploration in urban settings.