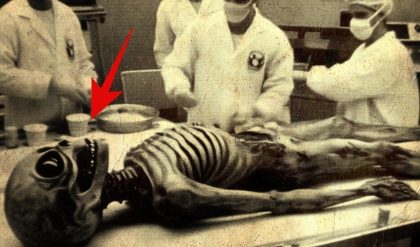
In a groundbreaking archaeological find, researchers in East Africa have uncovered the remains of a colossal horned skeleton, shedding light on a previously unknown chapter of prehistoric life. This discovery has ignited excitement and curiosity within the scientific community, offering new insights into ancient megafauna and the ecosystems of the distant past.
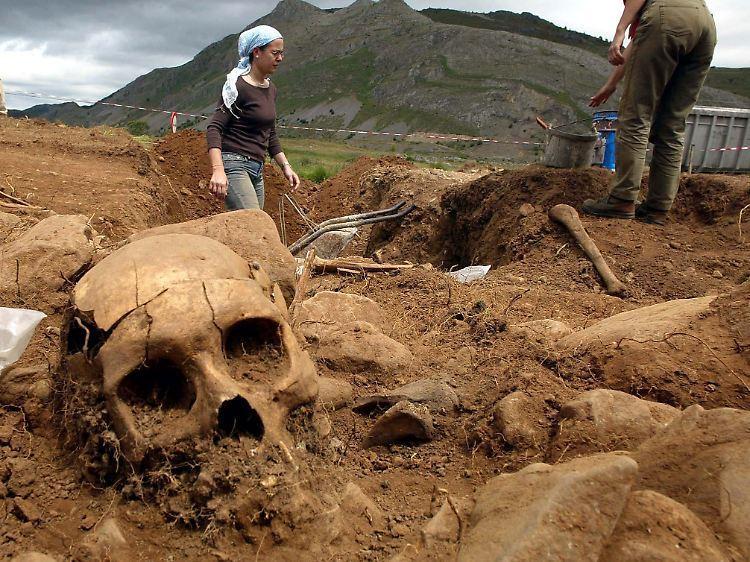

The Discovery
The giant horned skeleton was unearthed in a remote region of East Africa during a routine excavation by a team of paleontologists and archaeologists. The site, characterized by its rich fossil deposits and ancient sediment layers, has long been a focus of research into prehistoric fauna. However, the discovery of this unusually large and well-preserved skeleton has surpassed all expectations.
The skeleton was found partially embedded in the sediment, with its distinctive features, including large, curved horns, immediately drawing attention. Preliminary assessments suggest that the creature lived millions of years ago, during a period when East Africa was home to a diverse range of megafauna.
The Skeleton’s Features
The skeleton’s most striking feature is its enormous horns, which are estimated to be several feet long and curve dramatically outward. These horns, along with the creature’s large size, indicate that it was a formidable presence in its ancient environment. Additional features of the skeleton include robust limbs and a massive body, suggesting that the creature was both powerful and well-adapted to its surroundings.
Researchers have identified the skeleton as belonging to an unknown species, distinct from any previously documented prehistoric animals. The creature’s unique combination of physical traits has led scientists to speculate about its role in the ancient ecosystem and its possible interactions with other megafauna of the time.

Scientific Implications
The discovery of the giant horned skeleton has significant implications for our understanding of prehistoric life in East Africa. The presence of such a large and unique creature provides valuable information about the biodiversity of the region and the evolutionary processes that shaped ancient megafauna.
Researchers are conducting detailed analyses of the skeleton to learn more about its anatomy, diet, and behavior. Carbon dating and other methods will help determine the exact age of the fossil and provide insights into the environmental conditions that existed during the creature’s time.
The Ecosystem of Ancient East Africa
The giant horned skeleton offers a glimpse into the diverse and complex ecosystems that once existed in East Africa. During the period when this creature lived, the region was characterized by a variety of large herbivores and predators, including early forms of elephants, rhinos, and big cats.
The discovery helps fill in gaps in the understanding of how these ancient ecosystems functioned and how different species interacted with one another. It also contributes to the broader knowledge of how climate and environmental changes influenced the evolution and extinction of megafauna.
Conservation and Future Research
The site where the skeleton was discovered is now a focus of ongoing research and conservation efforts. Preserving the site and its fossil deposits is crucial for future studies and for protecting the delicate remains from potential damage.
The discovery has also sparked interest in further exploration of the region, with researchers planning additional excavations to uncover more fossils and artifacts. These efforts aim to build a more comprehensive picture of prehistoric life in East Africa and to discover more about the ancient creatures that once roamed the land.
Conclusion
The discovery of the giant horned skeleton in East Africa represents a remarkable breakthrough in the study of prehistoric life. The skeleton’s unique features and the insights it provides into ancient ecosystems underscore the richness and complexity of the region’s megafauna. As researchers continue to study this extraordinary find, it promises to enhance our understanding of the distant past and the diverse creatures that once inhabited the world.